3.Altimeter setting procedures
3.1General
These procedures apply to all flights. Exceptions and conditions may be determined by appropriate ATS unit.
Procedures describe the method for providing adequate vertical separation between aircraft and for providing required terrain clearance during all phases of a flight. This method is based on the following provisions:
3.1.1Transition altitude (TA)
Transition altitude is the altitude at or below which the vertical position of an aircraft is controlled by reference to altitudes. The transition altitude within all FIR is 5000 ft (1500 m) AMSL, except as stated below.
Outside TMA in mountainous areas where terrain exceeds 4000 ft (1200 m) AMSL, the transition altitude for all VFR flights and for IFR flights outside ATS routes is increased to an altitude identical to the height 1000 ft (300 m) AGL.
3.1.2Transition level (TL)
Transition level is the lowest flight level available for use, located at least 1000 ft (300 m) above the transition altitude.
3.1.3Transition layer
The airspace between the transition level and the transition altitude is called the transition layer. En-route horizontal flight is not permitted within the transition layer except especially approved activities (see AIP CR ENR 1.7.2.1). Minimum depth of transition layer is set to 1000 ft (300 m) in accordance with ICAO Doc. 7030/5.
3.2References to the vertical position
3.2.1The vertical position of aircraft shall be expressed in terms of:
- flight levels for flight at or above the transition level;
- altitudes for flight at or below transition altitude;
- heights above the ground for en-route flight up to 1000 ft (300 m) above the ground;
3.2.2While passing through the transition layer, vertical posotion shall be expressed in term of:
- flight levels when climbing; and
- altitude when descending.
3.3The change in reference from altitude to flight levels and vice versa
The change in reference from altitude to flight levels and vice versa is made:
- at the transition altitude when climbing; and
- at the transition level when descending.
3.4Description of altimeter setting region and procedures for pilots
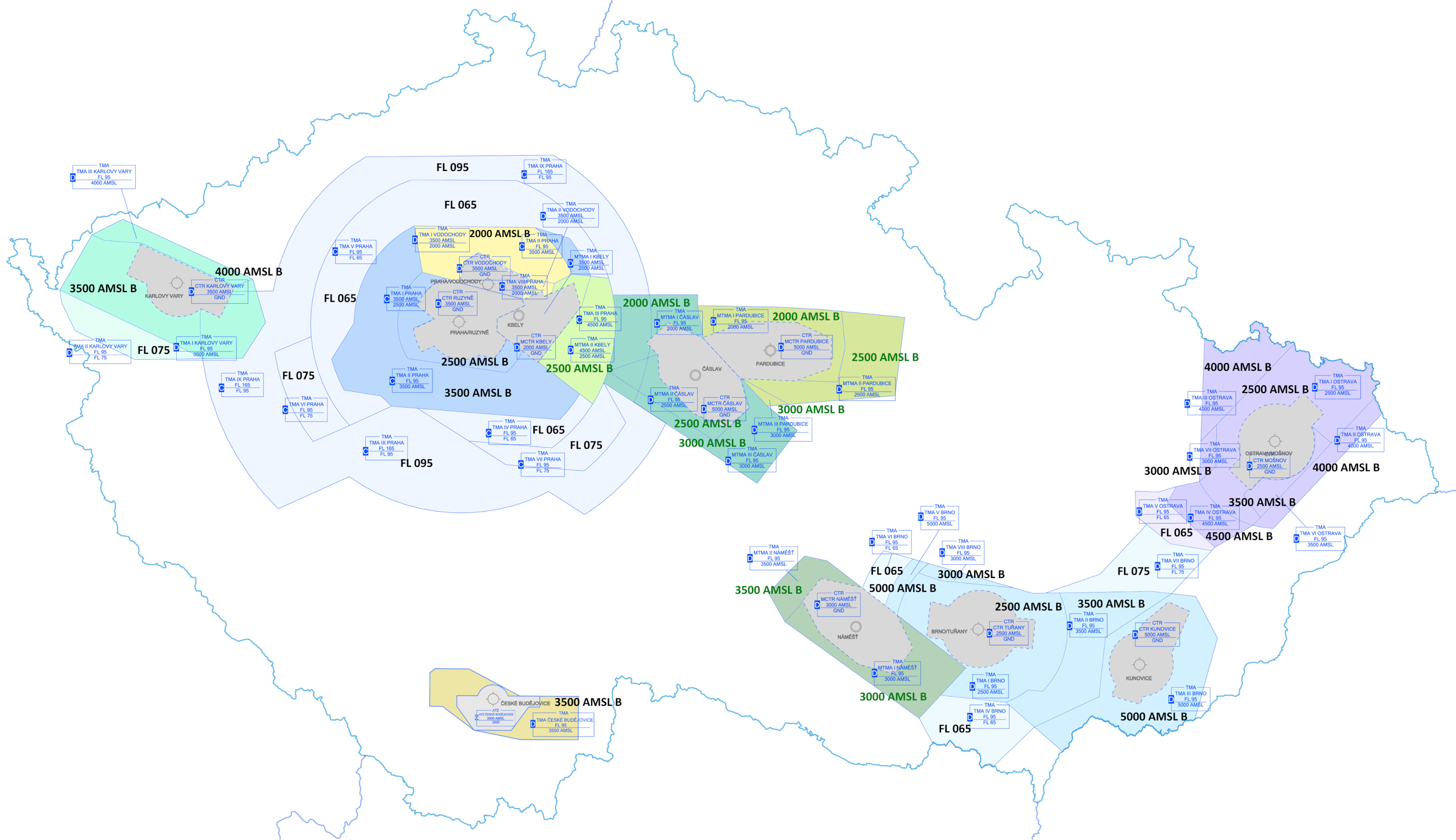
3.4.1During flight at or below the transition altitude the QNH shall be set as follows:following pressure shall be set on altimeters for the areas listed below:
- QNH of the controlled aerodrome
- within CTR, TMA and within such an ATZ whose upper limit or its part is identical with lower limit of TMA,
- below the TMA lower limit which is defined by altitude (AMSL)*.
Note 1: * Lower limit of TMA defined by altitude (AMSL) is always related to the QNH of the controlled aerodrome to which TMA belongs.
Note 2: * It concerns flights in the airspace just below the lower limit of TMA, during which it could come to unintended and undesirable penetration of TMA or which could cause an improper pressure altitude data display on the ATS surveillance systems, when the pressure is set up incorrectly.
The airspace area below the TMA lower limit defined by AMSL is depicted in the “TMA with lower limit defined by AMSL” chart.
- regional QNH or QNH of the nearest uncontrolled aerodrome
- in other cases.
Note: Regional QNH is a forecast of the QNH minimum value within FIR Praha for a specified time period.
- in other cases.
- Within the CTR - QNH of the applicable controlled aerodrome
- Within the TMA or below the TMA - QNH of the specified aerodrome
- Within the ATZ whose upper limit or its part is identical with lower limit of TMA - QNH of the specified aerodrome
- Within the ATZ laying completely or partially bellow a TMA, but without a direct border with the TMA - QNH of the applicable uncontrolled aerodrome* otherwise QNH of the specified aerodrome
- In other ATZ - QNH of the applicable uncontrolled aerodrome* otherwise regional QNH
- In other cases - regional QNH
"QNH of the specified aerodrome" for the purpose of TMA is:
- TMA Brno - QNH LKTB
- TMA České Budějovice - QNH LKCS
- TMA Karlovy Vary - QNH LKKV
- TMA Ostrava - QNH LKMT
- TMA Praha - QNH LKPR
- TMA Vodochody - QNH LKVO
- MTMA Čáslav - QNH LKCV
- MTMA Kbely - QNH LKKB
- MTMA Náměšť - QNH LKNA
- MTMA Pardubice - QNH LKPD
In case of more overlapping TMAs, pilot flying below such TMAs shall use the QNH of the lowest TMA.
* Note: if the "AFIS" or the "information to known traffic" u nits are operational.
The airspace area below the TMA lower limit defined by AMSL is depicted in the “TMA with lower limit defined by AMSL” chart.
3.4.2Information on the aerodrome QNH, temperature and transition level in TMA is provided in ATIS broadcasts or transmitted by the appropriate ATS unit. Regional QNH is provided in MET broadcasts and is available on request from the ATS units.
3.4.3QNH values are given in hectopascals. QNH in milimetres Hg is provided on request. Minimum flight altitudes are published in appropriate charts.
3.4.4VFR flights up to an altitude of 5000 ft (1500 m) AMSL or up to a height 1000 ft (300 m) AGL, if this level exceeds 5000 ft (1500 m) AMSL, shall set the altimeter to the QNH in accordance with paragraph 3.4.1.
3.5Flight planning
Levels at which a flight is to be conducted shall be specified in a flight plan:
- flight levels for flight at or above the lowest usable flight level or above transition altitude;
- altitudes for flight at transition altitude or below;
- abbreviation VFR for uncontrolled VFR flights.
3.6Procedures in controlled airspace
3.6.1If a VFR flight within controlled airspace is cleared by ATC to an altitude which the pilot finds unacceptable he/she shall request an alternative altitude. If such a request is not received ATC will consider that the clearance has been accepted and will be complied with.
3.6.2Vertical separations
Vertical separation from IFR flights is provided within controlled airspace Class C by assignment of different levels. ATC unit may clear VFR flight to level which is specified for IFR flight.
3.7Table of cruising levels
All en-route VFR flights shall be operated in VFR cruising levels corresponding to the flown track according to table of cruising levels stated below. However ATC unit providing service in controlled airspace may also assign level that is specified for IFR flights.
| Table of cruising levels | ||||||||||||
| Magnetic track | ||||||||||||
| from 000° to 179° | from 180° to 359° | |||||||||||
| IFR | VFR | IFR | VFR | |||||||||
| FL | m | ft | FL | m | ft | FL | m | ft | FL | m | ft | |
| - | 900 | 3000 | - | 1050 | 3500 | - | 1200 | 4000 | - | 1350 | 4500 | |
| 50 | 1500 | 5000 | 55 | 1700 | 5500 | 60 | 1850 | 6000 | 65 | 2000 | 6500 | |
| 70 | 2150 | 7000 | 75 | 2300 | 7500 | 80 | 2450 | 8000 | 85 | 2600 | 8500 | |
| 90 | 2750 | 9000 | 95 | 2900 | 9500 | 100 | 3050 | 10000 | 105 | 3200 | 10500 | |
| 110 | 3050 | 11000 | 115 | 3500 | 11500 | 120 | 3650 | 12000 | 125 | 3800 | 12500 | |
| 130 | 3950 | 13000 | 135 | 4100 | 13500 | 140 | 4250 | 14000 | 145 | 4400 | 14500 | |
| 150 | 4550 | 15000 | 155 | 4700 | 15500 | 160 | 4900 | 16000 | 165 | 5050 | 16500 | |
| 170 | 5200 | 17000 | 175 | 5350 | 17500 | 180 | 5500 | 18000 | 185 | 5650 | 18500 | |
| 190 | 5800 | 19000 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
3.8Transition levels according to the current QNH
| QNH in hPa | Transition level |
| ≥ 1051 | 50 |
| 1014-1050 | 60 |
| 978-1013 | 70 |
| ≤ 977 | 80 |




 PDF/Print
PDF/Print